 Rocks and Minerals
Rocks and Minerals
Rocks and Minerals
Rocks and Minerals







 Rocks and Minerals
Rocks and Minerals
Rocks and Minerals
Rocks and Minerals

Study the lesson for one week.
Over the week:

Physical Characteristics
Locations
Activity 1: Narrate the Lesson
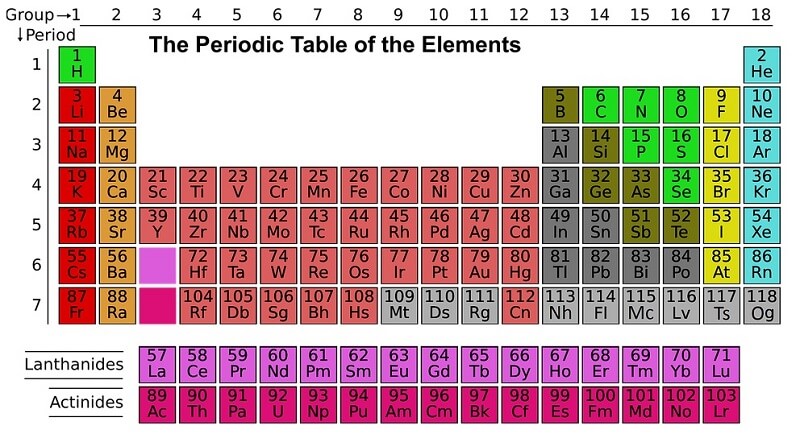
Activity 2: Can You Find It?
Find the following elements on the periodic table:
Activity 3: Map the Lesson
Activity 4: Take a Nature Walk
Activity 5: Complete a Field Book Entry

After your nature walk, complete page 6 in 'Fifth Grade Science Rocks and Minerals Notebook Pages.'